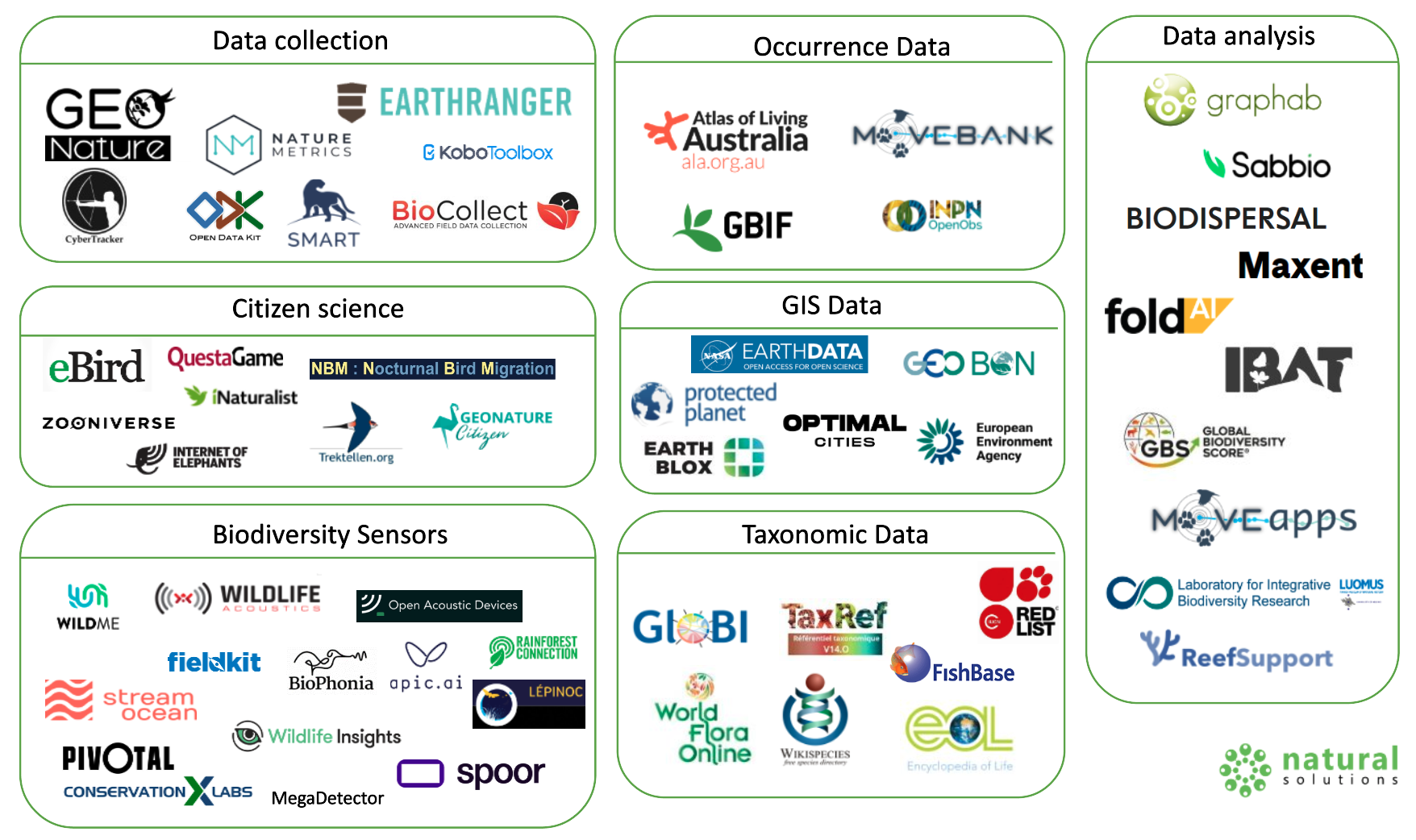
Biodiversity Tech Landscape 2023
As our world becomes more connected, the role of software in protecting biodiversity becomes increasingly important. By using its abilities to analyze data, create models, monitor situations, foster collaboration, and provide education, we can make smart choices and take early actions to make sure that the diverse range of life on our planet keeps flourishing for future generations.
Our goal is to create a comprehensive data system that brings together various digital tools designed for preserving biodiversity (such as data collection, citizen science software, automatic biodiversity sensors, and more). This way, anyone – whether an individual or an organization – who wants to help protect biodiversity can find and use specific tools that suit their needs. We welcome you to add your digital solutions or any useful ideas to our directory, so they can be shared with the entire community.
Tell us about your platform
As species face unprecedented threats from climate change, habitat loss and pollution, innovative solutions are needed more than ever. Here, we explore how software is playing a pivotal role in helping biodiversity thrive:
Data Collection : Software applications are revolutionizing the way we collect biodiversity data. From mobile apps that allow scientists to record sightings of rare plants and animals, to advanced machine learning algorithms software that enable us to amass vast amounts of data. This data, in turn, helps scientists and conservationists gain insights into species distributions, population trends, and ecosystem health.
Citizen science software refers to digital tools and platforms that enable individuals, often non-professional scientists or enthusiasts, to actively participate in scientific research and data collection. These software applications facilitate collaboration between scientists and volunteers by allowing them to contribute to various research projects, monitor environmental conditions, record observations, and gather data that can be used for scientific analysis.
Automatic Biodiversity Sensors are advanced technological devices designed to monitor and assess various aspects of ecosystems and biodiversity without human intervention. These sensors utilize a combination of technologies such as cameras, microphones, temperature and humidity sensors, and more, to collect real-time data on species behavior, environmental conditions, and ecosystem health.
An Occurrence Database in the context of biodiversity refers to a structured and organized collection of records documenting the presence of various species at specific locations and points in time. These databases serve as repositories of valuable information about the distribution, abundance, and occurrence of different organisms within their natural habitats.
Taxonomic data refers to information about the classification and categorization of living organisms into different taxonomic groups based on their evolutionary relationships. These groups, or taxa, include categories like kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Taxonomic data provides details about the characteristics, relationships, and distribution of various species, helping scientists and researchers understand biodiversity, evolutionary history, and ecological interactions.
GIS Data Geographical Information Systems (GIS) software is a game-changer in biodiversity conservation. It helps experts create detailed maps that highlight areas of high biodiversity, critical habitats, and migration corridors. These maps are invaluable tools for making informed land-use decisions, designing protected areas, and planning wildlife corridors to connect fragmented habitats.
Biodiversity data analysis involves the systematic examination of information related to the variety of life forms within ecosystems. This process employs statistical and computational techniques to derive insights, patterns, and trends from collected biodiversity data. By analyzing factors such as species distribution, abundance, interactions, and environmental conditions, researchers gain a deeper understanding of ecosystem dynamics and can make informed conservation and management decisions. Biodiversity data analysis plays a critical role in uncovering the complexities of life on Earth and guiding efforts to preserve and protect our planet's rich biological heritage.
This is a first draft if you see something missing we will be very happy to hear about it.
Let’s do it together !